Free home visits
with a local audiologist

Head of Online Medical Content

Audiology Expert at Hearing Aid UK

Overview | Ear congestion | Why do ears block? | Symptoms | Causes | How can you unblock your ear? | Treatment | Conclusion
Blocked ears occur when the eustachian tube, connecting the middle ear to the back of the nose, becomes obstructed. Causes include allergies, colds, or sinus infections, leading to pressure buildup and temporary hearing loss. Remedies include swallowing, yawning, or using decongestants to relieve the blockage and restore normal hearing.
In this article, we will delve into the reasons why ears become blocked, exploring both common and uncommon factors, as well as providing insights into how to prevent and address this nagging problem to restore clear and comfortable hearing.
Experiencing blocked ears can be an uncomfortable and disconcerting sensation, often leading to impaired hearing and discomfort. There are various causes behind this common issue, ranging from simple, temporary factors like earwax buildup or changes in air pressure, to more serious conditions such as infections or underlying medical conditions.
Ears can become blocked due to either excessive earwax accumulation or exposure to high altitudes. However, in certain instances, a more serious underlying cause may be responsible for this discomfort. Understanding the root causes of ear blockage is essential for effective treatment and relief as well as helping your GP prevent future ear problems.
Ear feel blocked? Waking up with blocked ears? Blocked ears, also known as ear congestion or ear blockage, can be a common and annoying problem that can affect people of all ages. It is often caused by a build-up of fluid or wax in the ear canal, but it can also be caused by a variety of other factors.
Something as simple as a change in the weather might cause ear blockage, as you are naturally more prone to allergy and ear troubles during the colder months. You might have blocked ears without any pain or discomfort - either way - it is still an annoyance when sounds become muffled and distorted and you are left feeling like you are straining to hear.
Whether it is your left, right or both ears blocked - ear blockages can be rather a serious annoyance with scope to be a genuine health risk, so when a blockage does appear (especially out of the blue) it's not always due to earwax.
You might have many questions like "Why is my ear blocked?", "What are the causes of blocked ear" and "Are blocked ears treatable?". Before treating blocked ears, it is useful to educate yourself on the causes and how we can prevent this in the future.
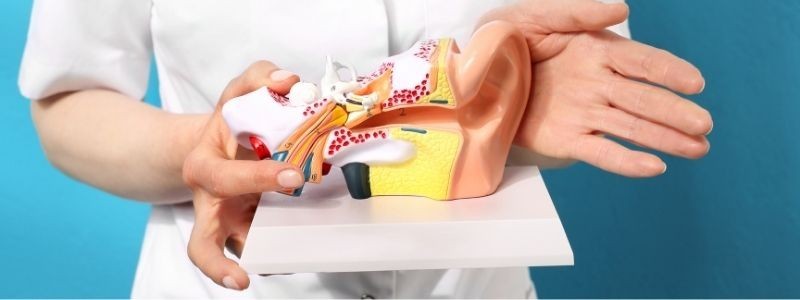
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction or ETD is one of the main causes of a blocked ear and this tube attaches your middle ear to your throat. You might already know, but this tube is where fluid or mucus goes from your ear to the back of your throat - which you then swallow.
When your Eustachian tube is blocked the fluid can't naturally flow and can become trapped in your middle ear and then cause blockage to your ear. Blocked ears usually come hand in hand with various infections like sinusitis (sinus pressure).
There are other ailments that are brought on by infection, such as coughing, runny nose, sneezing, blocked ears, and sore throat. It is important to unblock your ears as soon as you can, as prolonged trapped fluid in your ear can cause ear infections - which is a build-up of bacteria or a viral infection that reaches your middle ear.
Other symptoms of ear blockage caused by allergies or ear infections include: a runny nose, coughing, sneezing, and sore throat.

This is caused by sinus troubles, colds, and flu. All these nasties make your Eustachian tube to swell and can result in a blockage. Because of the swelling, the tube cannot do its job of flushing fluid and keeping the air flowing. This means that the inner ear and middle ear cannot work properly and can reduce your ability to hear.
This is when you get a tear in your eardrum (that separates your middle ear and outer ear). This in turn can cause infections and block your Eustachian tubes, as fluid can build up over time.
Sometimes a growth in the back of the nose, like adenoids, can obstruct the opening of the Eustachian tube - causing a blockage.
Blocked ears after swimming? If you are a keen swimmer, you probably know that swimming can cause ear infections if you don't dry your ears properly afterwards, as water can stay in your ears. This is also known as 'swimmer's ear' or Otitis Externa, where bad bacteria and fungus can develop over time. This is also calledan outer ear infection.
Otitis media is an infection of the middle ear that results in inflammation and a build-up of fluid behind your eardrum. Although anyone can get a middle ear infection, children are more prone to this type - especially babies and toddlers.
There are some signs to look out for that can indicate you have an ear infection. These are fever, fluid leaking from your ears, ear pain, and redness. If you have used a cotton swab to try and unclog any blockages beforehand, this might be the reason why you are now experiencing pain.
Most of the time plugged ears are caused by Eustachian Tube Dysfunction, but sometimes someone who complains of a continual ear-plugging sensation and increased sensitivity to sound can mean you have hyperacusis.
However, the main causes of hyperacusis are loud noise exposure and ageing, but if you have a blocked ear feeling and you find yourself more sensitive to noise - you need to seek medical help as soon as you can to get a diagnosis and be administered the right treatment if needed.

Your earwax does a great job of protecting your ears by naturally cleansing your ear canal so that it stops anything from entering your ears. It is usually soft, but it can become hard and therefore block your ears over time.
Do ears feel clogged and ringing? If you are experiencing dizziness, ringing in the ear or earache you might have hardened wax that's blocking your ear. Blocked ear wax needs to be treated immediately, as it can cause serious damage. This type of buildup can also limit your hearing abilities and can if left untreated for a long period of time, cause permanent hearing loss.
The main symptoms of earwax buildup are usually earache, hearing problems, blocked ear feeling, tinnitus (ringing in the ear), coughing, or discharge from the ear.
You can also develop temporary ear blockage troubles when you are walking or driving up a mountain, flying, or scuba diving. This is because when you experience a quick shift in air pressure outside your body - your ears can become blocked or feel clogged up.
Let me explain, your Eustachian tube has many roles, and one is to stabilise the pressure in your middle ear. As altitude grows it sometimes can't stabilise pressure successfully and you can then feel the increased air pressure in your ears giving you a blocked ear feeling.
Unfortunately, high altitude conditions can sometimes get too much for the rest of your body to cope with and you can experience dizziness, sickness, shortness of breath, and headaches.
Your ear can feel blocked or can ring after you've experienced an evening of loud live music. This should clear within two days.
This is a benign ear growth on the cranial nerve leading from your inner ear to your brain. These growths are generally quite slow to develop and not big, but even though they are small they can still inflict pressure on the nerves in your inner ear. This usually results in a blocked ear, ringing in the ear, and hearing loss.
Other less common causes of blocked ears are anxiety, Meniere's disease, and other balance disorders.

Your ears might unblock themselves on their own over the course of a few days, but there are other options to consider that can relieve blocked ears that you can do at home. There are a few blocked ear treatments out on the market today - some are even in your own kitchen cupboard!
Earwax does a great job of protecting your ear by cleansing your ear canal and preventing foreign objects and debris from entering the ear. It is usually soft but can harden over time and cause your ears to block.
You can normally treat excess wax at home. Try two to three drops of virgin olive oil in the ear(s) that are blocked or baby oil into your ears to try and soften your earwax and dislodge any blockage. Remember to tilt your head for a minute or so after you have put the drops in, so your ears have a chance to flush out anything.
You can source over-the-counter remedies that can help un-clog your ears due to sinus troubles, colds, or common allergies. These are normally decongestants like antihistamines - always check with your pharmacy on the best solution for you with your health history in mind.
Inhaling steam is a common blocked ears remedy you can do at home. It can sometimes help soften excess mucus in your ears. This could be sitting in your bathroom with your shower on extra hot or pouring hot water into a bowl, putting your head over the top, and covering it with a towel. Placing hot face clothes over your ears can sometimes help loosen ear mucus too.

At the end of the day, it is always best to contact a professional - either through your local NHS clinic or private practice - to diagnose the cause of your ear blockage. Do not attempt to try any other at-home remedy beyond what we have suggested you can do safely. See a doctor if you cannot unclog your ears with the suggested home remedies.
If you have an Eustachian tube blockage, your GP might prescribe you medications such as: antibiotics, and antihistamines. If you have pain with your blocked ear, your GP might recommend over-the-counter pain relief such as: ibuprofen, Acetaminophen, and Naproxen sodium.
Your local audiologist can help you with your blocked ears and will give you more information on blocked ears after a cold, blocked ears and headache, blocked ears and dizziness, blocked ears and sinus troubles, and more symptoms.
If you have blocked ears due to excessive earwax and would like advice on how to clear a blocked ear and the best treatment with a local audiologist - our consultations can be performed at one of our clinics or a home visit and will take around 10 to 15 minutes per ear.
We offer traditional syringing, the more popular micro-suction, or even endoscopic suction. The cost is from £40 for one ear or £60 if both ears need doing.
In general, it is important to be gentle when attempting to relieve ear congestion. Avoid inserting objects, such as cotton swabs or hairpins, into the ear canal, as this can cause injury or further irritation. If the congestion persists or is accompanied by other symptoms, such as pain or discharge, it is important to see a healthcare provider for further evaluation and treatment.
If you can't unblock your ears, try swallowing, yawning, or chewing gum to open the Eustachian tubes. Use a nasal decongestant or saline spray if congested. Gently blow your nose while pinching your nostrils closed. If these methods don't work, seek advice from your local GP as we cannot help you.
However, if you'd like to book an appointment or would like to speak to an audiologist about your hearing healthcare - then please call us on 0800 567 7621
You can also watch the Healthline video about popping your ears or download the NHS whitepaper about ear health below.
 I have difficulty hearing in noisy places
I have difficulty hearing in noisy places  High-Pitched Sounds Like Birdsong Are Fading. Do I Have Hearing Loss?
High-Pitched Sounds Like Birdsong Are Fading. Do I Have Hearing Loss?  Asking people to repeat themselves frequently. Do I have hearing loss?
Asking people to repeat themselves frequently. Do I have hearing loss? Do not spend hundreds of pounds without getting a second opinion from us.
 Not only are the prices great, but the service is fantastic! Many thanks to your team.
Not only are the prices great, but the service is fantastic! Many thanks to your team.If you have tried home remedies or any of the advice we have talked about in this article and you still have blocked ears or a build-up of wax - you must arrange to see your local GP who will check your ears and then refer you to your ENT department if necessary.
If you have an Eustachian tube blockage your doctor might prescribe antibiotics, decongestants or anti-fungal medication. You might also be recommended a course of pain relief to accompany your prescribed medication, as often you can experience pain with blocked ears.
However, if you are diagnosed with an acoustic neuroma, you might be referred for surgery.
Blocked ears after COVID-19? Due to COVID being a respiratory virus, this means it can cause congestion, ear pain and sinus pressure - but it is important to remember these are not common symptoms of the virus.
COVID-19 generally causes fever, chills, cough, sore throat and fatigue. On the other hand, the Delta variant has been known to cause more common cold symptoms and that would include more earaches.
When we refer to a product as 'Latest Launch', we mean it is the latest to be released on the market.
When we refer to a product as 'New', we mean that the product is the newest hearing aid model on the market.
When we refer to a product as 'Superseded', we mean that there is a newer range available which replaces and improves on this product.
When we refer to a product as an 'Older Model', we mean that it is has been superseded by at least two more recent hearing aid ranges.